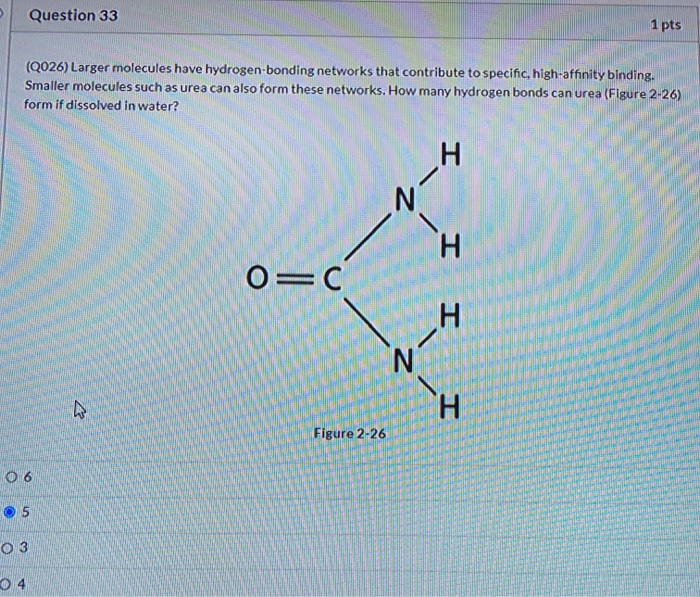
How Many Hydrogen Bonds Can Urea Form - Smaller molecules such as urea can also form. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate a total of 2 hydrogen bonds. Because of its chemical makeup, urea can generate five hydrogen bonds. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the 4 amide hydrogens), but only the carbonyl oxygen. The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with. Additionally, the carbonyl oxygen in urea can also.
Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the 4 amide hydrogens), but only the carbonyl oxygen. Smaller molecules such as urea can also form. Because of its chemical makeup, urea can generate five hydrogen bonds. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with. Additionally, the carbonyl oxygen in urea can also. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate a total of 2 hydrogen bonds.
Smaller molecules such as urea can also form. The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with. Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the 4 amide hydrogens), but only the carbonyl oxygen. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. Because of its chemical makeup, urea can generate five hydrogen bonds. Additionally, the carbonyl oxygen in urea can also. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate a total of 2 hydrogen bonds.
Hydrogen bonds during reverse osmosis filtration of urea molecules
Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the 4 amide hydrogens), but only the carbonyl oxygen. Smaller molecules such as urea can also form. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. The distinctive chemical.
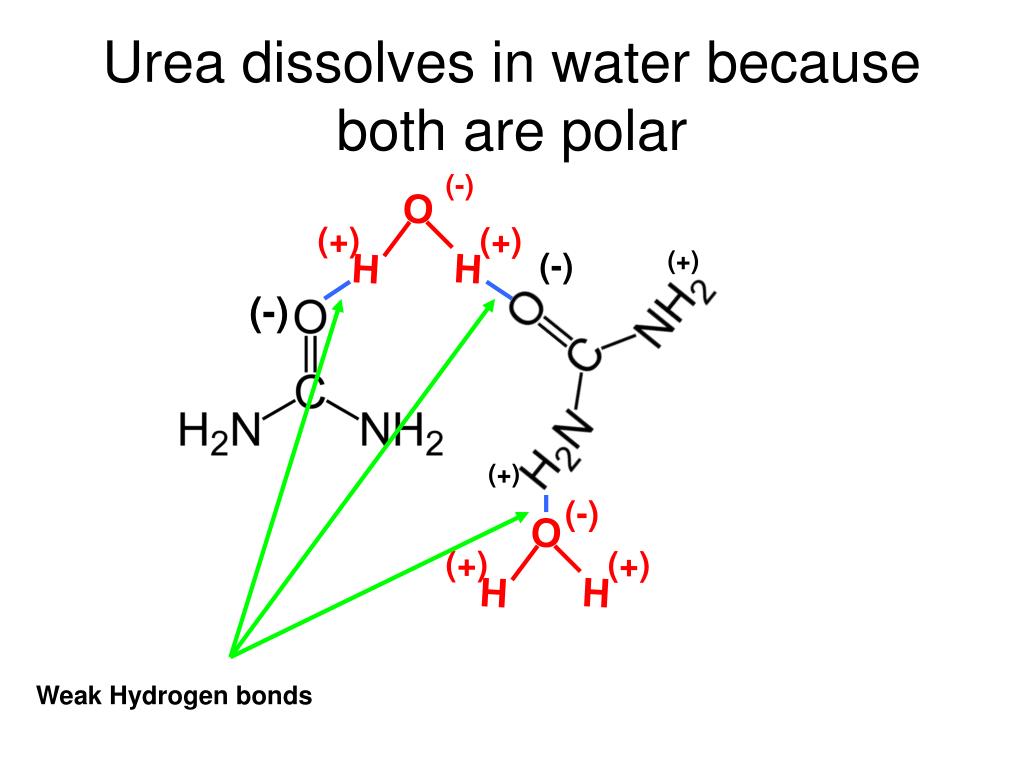
Postulated hydrogen bonds formed between urea, ChCl and water, (a
Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate a total of 2 hydrogen bonds. Additionally, the carbonyl oxygen in urea can also. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving.
Urea is an organic compound widely used as a fertilizer. Its solubility
The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with. Because of its chemical makeup, urea can generate five hydrogen bonds. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate a total.
How Many Hydrogen Bonds Can Urea Form
Smaller molecules such as urea can also form. Because of its chemical makeup, urea can generate five hydrogen bonds. The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with. Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the 4 amide hydrogens), but only the carbonyl oxygen. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea,.
PPT Chapter 22 Properties of Water PowerPoint Presentation, free
Smaller molecules such as urea can also form. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate a total of 2 hydrogen bonds. The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with. Because of its chemical makeup, urea can generate five hydrogen bonds. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule,.
(a) Hydrogen bonding around a urea molecule in the UC cocrystal. (b
Additionally, the carbonyl oxygen in urea can also. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with. Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the 4.
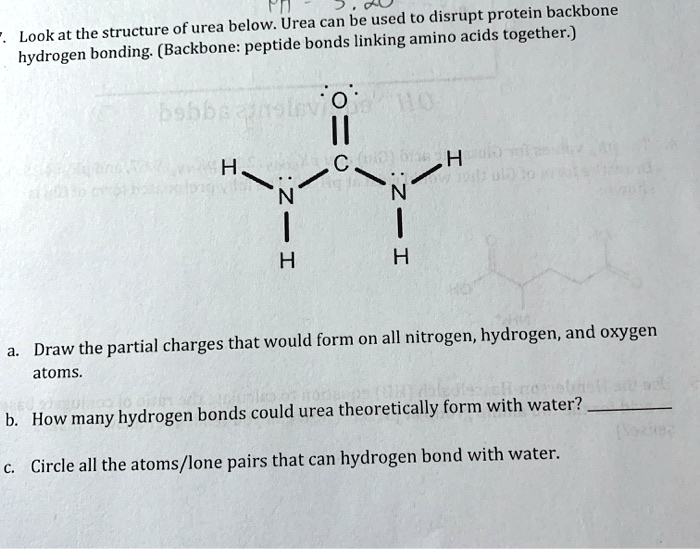
SOLVED Fn can be used to disrupt protein backbone. Look at the
The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with. Smaller molecules such as urea can also form. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. Additionally, the carbonyl oxygen in urea can also. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea,.
The Excretory System. ppt download
Because of its chemical makeup, urea can generate five hydrogen bonds. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate a total of 2 hydrogen bonds. Urea, in principle, can form 6.
[GET ANSWER] 8. Urea is a watersoluble product of nitrogen metabolism
Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the 4 amide hydrogens), but only the carbonyl oxygen. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate.
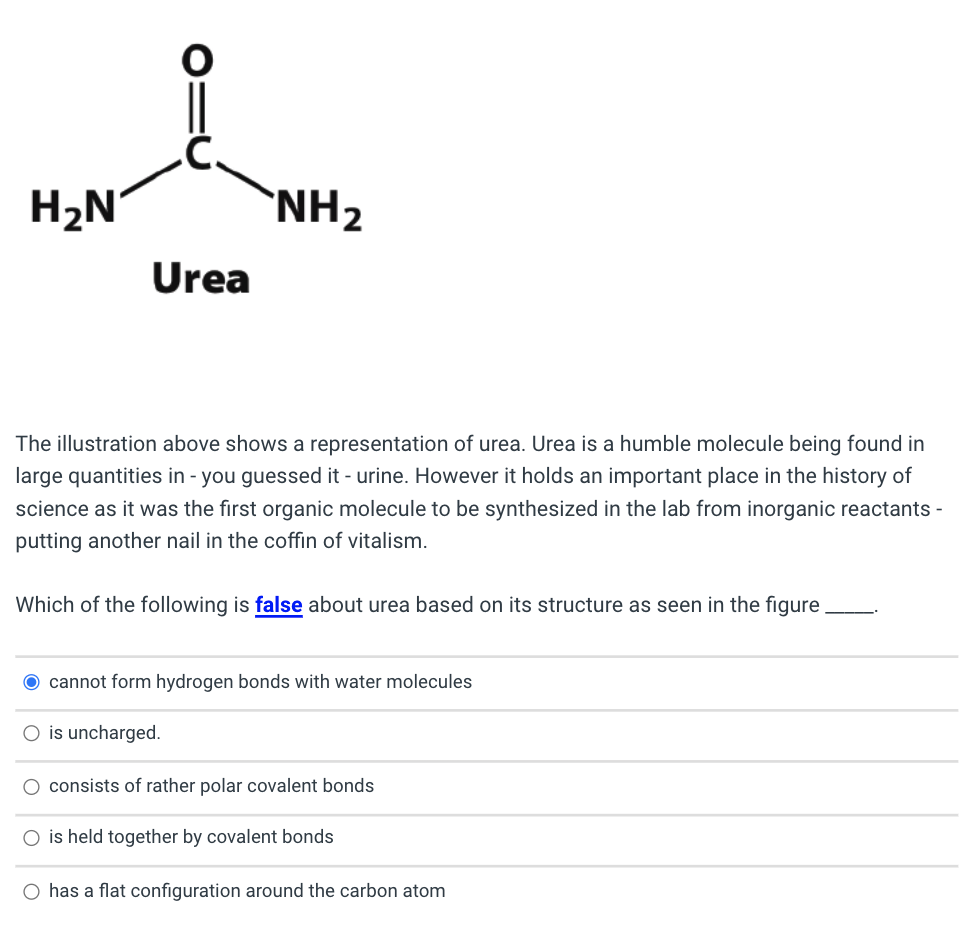
Solved H2N NH2 Urea The illustration above shows a
In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other. Additionally, the carbonyl oxygen in urea can also. Because of its chemical makeup, urea can generate five hydrogen bonds. Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the.
Because Of Its Chemical Makeup, Urea Can Generate Five Hydrogen Bonds.
Since there are two nitrogen atoms in urea, it can donate a total of 2 hydrogen bonds. Smaller molecules such as urea can also form. Urea, in principle, can form 6 hydrogen bonds (involving both its carbonyl oxygen and the 4 amide hydrogens), but only the carbonyl oxygen. In urea, each nitrogen atom can form a hydrogen bond with a water molecule, and the oxygen atom can form two hydrogen bonds with two other.
Additionally, The Carbonyl Oxygen In Urea Can Also.
The distinctive chemical characteristics of urea and its interactions with.





![[GET ANSWER] 8. Urea is a watersoluble product of nitrogen metabolism](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/6da2255547ef4048a23b3f1dd9991c8f.jpg)